-
1 基本概念
-
2 PPT
Chapter 8 Foreign Exchange Risk and Forecasting
Ⅰ Types of foreign exchange risk
A. Foreign Exchange Risk
Foreign exchange risk – the variability of the firm’s value arises from uncertainty about thefuture exchange rates.
Foreign Exchange Risk Exposure – the degree to which a company is affectedby exchange rate changes.
International assets and liabilities inforeign currencies could bring profits or losses to the firm depending on thefuture directions of exchange rates.
B. Three Types of Foreign Exchange Risk
1. Translation exposure
Accounting exposure from translatingfinancial statement from one currency to another currency.
2. Transaction exposure
Exposure from the uncertain currency value ofa foreign-denominated transaction to be completed at some future date.
3. Economic exposure
Exposure from changes in exchange rates tothe firm’s present value of future cash flows.
Ⅱ How to hedge against risks
A. How to manage exposure?
Goal: to reducevariability of consolidated earning, obligations, and cash flows from foreignsubsidiary to unanticipated changes in exchange rates.
B. How to reduce risk:
Hedge in forward, futures, or options markets
Invoice in the domestic currency
Rush payments of currencies expected to appreciate.
Rush collection of currencies expected to depreciate.
Ⅲ Foreign exchange risk premium
In the “uncovered interest rate parity,” weassume that the forward rate is the unbiasedpredictor of the future spot exchange rate.
A. Uncovered Interest Rate Parity
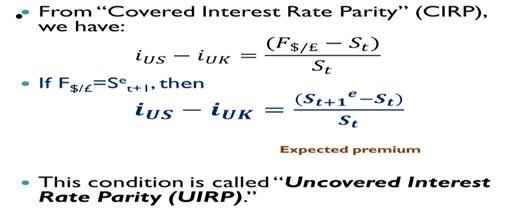
What if F$/£ ≠ Set+1

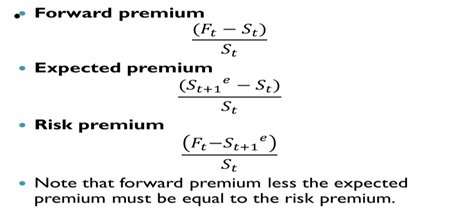
B. Computing the Risk Premium

C. Three types of premium (in percent)
Ⅳ Market efficiency
A market is efficient if prices reflect all available information.
That is, the forward and spot rates willquickly adjust to new information so that no investor can make profitconsistently from foreign exchange trading.
With the efficient market, the forward ratewould differ from the expected future spot rate only by a risk premium.
Ⅴ Foreign exchange forecasting
If a forward rate does not perfectly reflectthe expected future spot rate, whoever could forecast more accurately than therest of the market could make enormous profits.


