6.2 Exchange Rates, Interest Rates, and Inflation
-
1 基本概念
-
2 PPT
上一节
下一节
Ⅲ Interest rateand inflation: Fisher equation
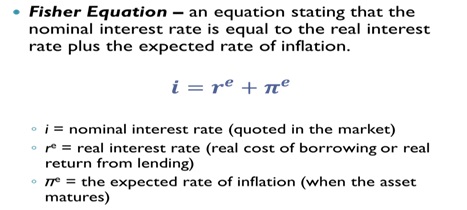
A. Fisher equation
B. Real Interest Rates Equalization
If we expect the real interest rate to behigh in a particular country, then investors would move investment funds intothat country. Therefore, we would predict that expected real interest rateswill be equalized across countries.
From this data, we would anticipate more capital flow into Brazil.
As investment funds leave the U.S. → sell bonds in U.S. causing rUS torise → buy bonds in Brazil causing rBRAZILto fall → rUS = rBRAZIL
Note that this is a speculative condition,but not an arbitrage condition. Thus, it does not need to hold.
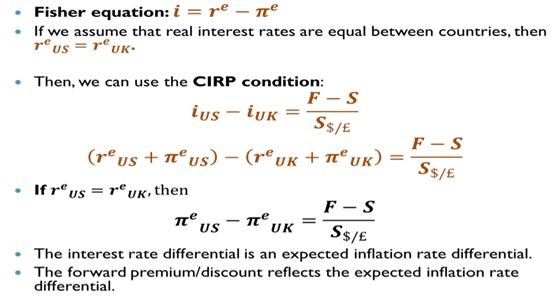
C. Connecting Fisher Equation to CIRP
D. Example:



